While varicose veins may not seem like a serious concern, they can sometimes be a symptom of deeper medical issues. Some individuals may experience only mild discomfort, while others develop symptoms that can turn into chronic venous insufficiency (CVI).
Recognizing which symptoms to monitor can help determine when varicose veins are more than just a cosmetic concern and may be a sign of vein disease. If left untreated, they can progress into more severe complications like blood clots, leg ulcers, or chronic pain—making it important to seek an accurate diagnosis before symptoms worsen.
Learn More About Chronic Venous Insufficiency
What Are Varicose Veins?
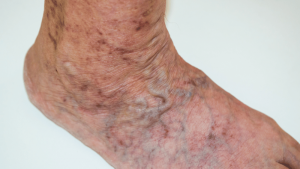
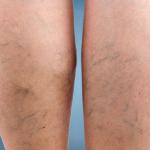
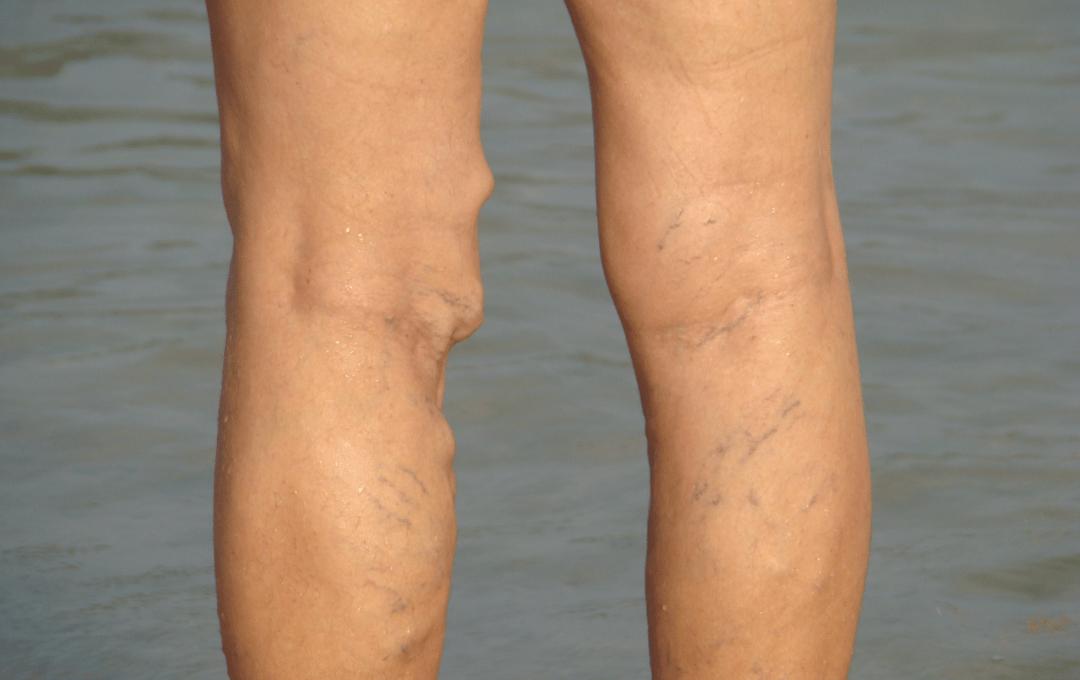
Varicose veins are swollen, twisted blood vessels that appear just beneath the skin’s surface. They may bulge in blue or purple rope-like patterns, typically on the lower legs, ankles, and feet.
What Causes Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins are caused by damaged or weakened vein valves. As the valves become damaged, blood will pool in the affected vein and increase pressure as a result. The affected vein will enlarge, leading to the bulging appearance you see from underneath the skin.
Certain risk factors can also contribute to the formation of varicose veins, including pregnancy, obesity, prolonged sitting or standing, genetics, and certain health conditions, such as diabetes. These contributing factors disrupt healthy blood flow by increasing pressure within the veins or weakening the vein walls, which can lead to the formation and worsening of varicose veins.
Early Varicose Vein Symptoms
Varicose veins don’t always cause pain, but other vein-related symptoms can still affect your daily comfort and quality of life.
Some of these varicose vein symptoms include:
- Achiness or heaviness in your legs, especially after standing
- Any swelling in your lower legs, feet, or ankles
- Itching or irritation around the vein
- Bulging, twisted, or enlarged veins
Varicose vein symptoms often progress over time if left untreated, making early diagnosis and treatment important to prevent further vein damage. Our symptoms quiz can help assess your vein health and take the first step toward getting a proper diagnosis. If you’ve started to notice worsening symptoms or new areas of concern, it may be time to speak with a vein specialist.
Relief is a Click Away – Book a Consultation Now
When To Be Concerned About Varicose Veins
In many cases, varicose veins progress beyond surface-level issues, leading to more advanced stages of vein disease.
Here’s when to worry about varicose veins and seek medical help:
- Skin ulcers form on the legs that are slow to heal
- Persistent pain, swelling, or burning in the leg
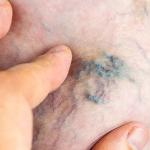
- Tenderness, pain, redness, or swelling of the affected area, which may indicate superficial thrombophlebitis (vein inflammation and clotting)
- Any changes in skin texture or color, like thickening, scarring, or discoloration
These symptoms can indicate chronic venous insufficiency or an increased risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which can lead to a pulmonary embolism. If you notice any varicose vein symptoms, seek a professional evaluation from a vein specialist. USA Vein Clinics’ physicians use a patient-centered approach to ensure that patients receive comprehensive and effective care.
How To Get Rid of Varicose Veins
USA Vein Clinics provides FDA-approved, minimally–invasive solutions to address varicose veins. These outpatient treatments don’t require general anesthesia, involve little recovery time, and have high success rates, according to multiple studies from the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
These varicose vein treatment options include:
- Endovenous Laser Treatment (EVLT): Uses laser energy to seal off damaged veins.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): Delivers heat via radiofrequency to close varicose veins.
- ClariVein®: A combination of mechanical and chemical methods to treat problem veins.
- Varithena: A specialized foam is injected into the vein so it collapses.
- VenaSeal™: Uses medical adhesive to close off the vein.
- Ultrasound-Guided Sclerotherapy: A targeted treatment using medical imaging to inject a solution into the vein.
In addition to these treatments, lifestyle changes —such as wearing compression stockings, regular exercise, and leg elevation—can support vein health and help reduce symptoms.
Ignoring varicose veins could lead to serious complications like blood clots, leg ulcers, and chronic pain. USA Vein Clinics’ experienced specialists provide a patient-centered approach to expert vein care, ensuring patients receive the best varicose vein medical procedure for their condition.
Book a consultation today and take the first step toward healthier legs and lasting pain relief.
Meet with a Vein Specialist Near You
FAQs
Are Varicose Veins Genetic?
If you have a family history of varicose veins, it can significantly increase your risk of developing them. If you have a family history or are concerned about your risk, consult a vein specialist to explore treatment options.
How to Prevent Varicose Veins?
Lifestyle changes such as regular movement, exercise, and a healthy diet can help prevent varicose veins and manage leg swelling, fatigue, and cramping. Elevating the legs and wearing compression socks can also help promote blood flow. To effectively address vein disease, it’s important to consult with a vein specialist about appropriate treatment options.
Are Varicose Veins Dangerous?
Varicose veins can be dangerous due to the serious health complications they can lead to, such as bleeding veins, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), venous ulcers, and lipodermatosclerosis. Visiting a specialist for an early diagnosis is key to avoiding these complications.
Do Varicose Veins Go Away?
Varicose veins typically do not go away on their own. They may worsen over time if left untreated, potentially leading to serious complications such as venous ulcers or deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Minimally–invasive treatments like sclerotherapy, endovenous laser treatment, and radiofrequency ablation are FDA-approved and highly effective in reducing symptoms.
Can Varicose Veins Cause Blood Clots?
Varicose veins may increase the risk of blood clots because poor circulation and blood pooling in the affected vein can promote blood clot formation. If you suspect a blood clot, seek prompt medical care.